What is meant by Locator in Selenium
Selenese commands are executed on the target element. The target element is defined in the web application based on the
locators. For example, suppose there is an link in the page with id as homepage, the link element will be located and identified by ‘id=homepage’ and then we can execute click command on the link homepage identified by locator ‘id=username’.
What are different locator types in Selenium IDE
The various locator types in Selenium IDE are as
follows:
- Locating
elements by ID – an element can be identified using the ‘id’ attribute defined for the object. Since it is assumed that id attribute is unique for an element in the page, hence element will be uniquely identified in
the page using id attribute for target. E.g. ‘id=iamunique’.
- Locating
elements by name – In case id attribute is not defined for the target element, we can identify the
element using name attribute in the target. E.g. ‘name = sonamgupta’. In case of object is not identified uniquely by name locator,
we can use multiple locators like ‘name =
sonamgupta value = bewafahai’ to uniquely identify the element.
- Locating
elements by link text – For link element, we can identify an element using
link text in the target. e.g. ‘link
=loginkaro’ will identify a link with text as loginkaro.
- Locating
elements by XPath – We can also use XPath to identify an element in the
page. XPath allows us to
query the DOM structure of the page like a XML document. For e.g. //input will
find first input box in the page and perform action on the same. Can use firepath/firebug to uniquely identify the element xpath
- Locating
elements by css – Elements in the webpage can be identified using CSS selectors to find
the objects that you need. Selenium is compatible with CSS 1.0, CSS 2.0, and
CSS 3.0 selectors. Syntax for identifying an element using css is ‘css = CSS Selector’
for e.g. ‘css=input.kyabaathain’ where
input is the tag name for element and kyabaathain is the classname. Both xpath and
css are useful to identify elements with complex identifiers.
Tools to identify the attributes
and locators for element in the webpage
We can identify element locators using different developer tools in different browsers. Below are some of the developer tools that
help to identify objects in the page.
- Firebug:
Firebug is a Firefox developer add-on used to identify elements on the page by
using the find functionality.
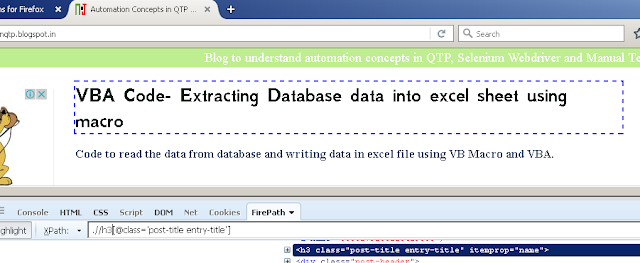
- FirePath: It is a Firefox add-on used with firebug and helps
in testing XPath and CSS on the page. Highlights all elements on the page that
match the selector to your element location.
- IE
Developer Tools: IE developer tools helps in identifying element. This is
inbuilt with IE browser and can be launched by pressing F12.
- Google Chrome Developer Tools: This is
inbuilt in Google chrome and can be launched by Pressing F12.
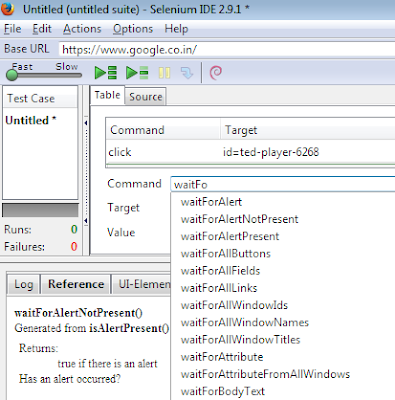 To wait for the element to appear in the page, there are different waitfor commands in selenium IDE, which waits for default timeout set up for the element to appear. So in case an element is not displayed straightway, waitfor commands can be used to resolve sync issues in selenium IDE.
To wait for the element to appear in the page, there are different waitfor commands in selenium IDE, which waits for default timeout set up for the element to appear. So in case an element is not displayed straightway, waitfor commands can be used to resolve sync issues in selenium IDE.